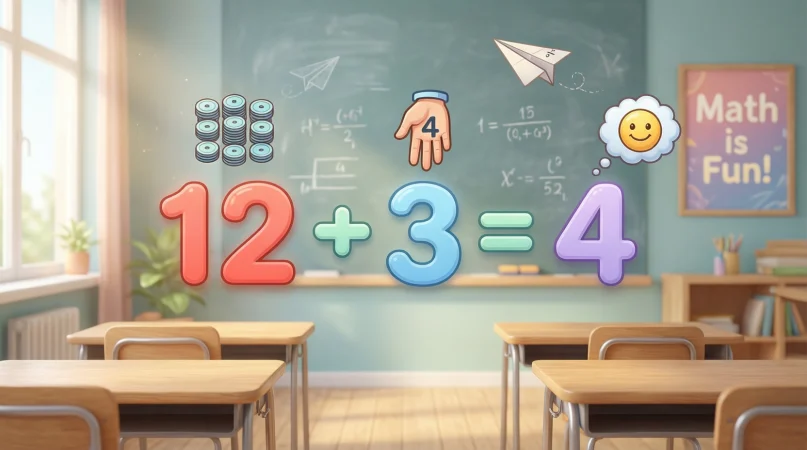If you’ve used long division, fractions, or even basic sharing problems, you’ve already worked with a dividend even if you didn’t realize it.
Understanding what does dividend mean in math is a foundational skill that makes division clearer, easier, and far less confusing. Whether you’re a student, teacher, parent, or someone brushing up on math basics, this guide will walk you through the concept step by step in plain, friendly language.
📌What Does Dividend Mean in Math?
In math, a dividend is the number that is being divided by another number.
It is the starting value in a division problem.
Example:
In the equation 20 ÷ 4 = 5,
- 20 is the dividend
- 4 is the divisor
- 5 is the quotient
Why Understanding the Dividend Matters
Division isn’t just about getting an answer it’s about understanding relationships between numbers. Knowing what the dividend is helps you:
- Read math problems correctly
- Avoid common calculation mistakes
- Understand fractions, ratios, and algebra
- Solve word problems more confidently
Once you grasp the dividend, the rest of division becomes much more logical.
The Basic Parts of a Division Problem
Before diving deeper, let’s quickly review all the key terms used in division.
The Four Main Parts of Division
| Term | Meaning | Example (20 ÷ 4 = 5) |
|---|---|---|
| Dividend | Number being divided | 20 |
| Divisor | Number dividing the dividend | 4 |
| Quotient | Result of the division | 5 |
| Remainder | What’s left (if not exact) | 0 |
📘 Memory Tip:
Dividend = “the number you divide.”
What Does Dividend Mean in Simple Words?
In everyday language:
- The dividend is the total amount
- The divisor is how many parts you split it into
- The quotient is how much each part gets
Simple Example:
If you have 12 apples and share them equally among 3 friends:
- Dividend = 12 apples
- Divisor = 3 friends
- Quotient = 4 apples each
🍎 12 ÷ 3 = 4
Origin and History of the Term “Dividend”
The word dividend comes from the Latin word “dividendum,” meaning:
“That which is to be divided”
How the Term Became Popular in Math
- Used in early arithmetic texts in Europe
- Became standardized as math education developed
- Widely adopted in schools, textbooks, and exams worldwide
Even today, the term remains essential in mathematics, accounting, economics, and computer science.
How the Dividend Is Used in Different Areas of Math
The concept of a dividend doesn’t stop at basic division. It appears in many areas of mathematics.
1. Basic Arithmetic
Used in simple division problems:
- 15 ÷ 5
- 100 ÷ 10
2. Long Division
The dividend is written inside the division symbol.
Example:
4 ⟌ 128
Here, 128 is the dividend.
3. Fractions
In a fraction:
- Numerator = Dividend
- Denominator = Divisor
Example:26
- Dividend = 6
- Divisor = 2
4. Algebra
Dividends can be numbers or expressions.
Example:(x2+6x+8)÷(x+2)
5. Polynomial Division
The entire polynomial being divided is the dividend.
Labeled Example Table: Understanding Dividend in Action
| Division Problem | Dividend | Divisor | Quotient | Remainder |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 18 ÷ 3 | 18 | 3 | 6 | 0 |
| 25 ÷ 4 | 25 | 4 | 6 | 1 |
| 100 ÷ 8 | 100 | 8 | 12 | 4 |
| 7 ÷ 2 | 7 | 2 | 3 | 1 |
Step-by-Step Example: Identifying the Dividend
Let’s break down a common math problem.
Problem:
45 ÷ 9 = ?
Step-by-Step:
- Identify the division sign (÷)
- The number before the sign is the dividend
- The number after the sign is the divisor
✔ Dividend = 45
✔ Divisor = 9
✔ Quotient = 5
Friendly, Neutral and Dismissive Usage Examples
Although “dividend” is a technical math term, it can still appear in different contexts.
Friendly / Educational Tone 😊
“Remember, the dividend is the number you start with in division.”
Neutral / Academic Tone 📘
“In this equation, the dividend is divided by the divisor to produce the quotient.”
Slightly Dismissive / Corrective Tone ⚠️
“No, 12 is the dividend not the divisor. Read the problem carefully.”
Common Mistakes Students Make with Dividends
Even though the concept is simple, mistakes happen often.
Frequent Errors:
- Confusing dividend with divisor
- Assuming the larger number is always the dividend
- Mixing up numerator and denominator
- Misreading word problems
How to Avoid Them:
- Look for words like “divided by”
- Identify the total amount first
- Rewrite word problems as equations
Dividend vs Divisor vs Quotient: Clear Comparison
| Term | Role | Question It Answers |
|---|---|---|
| Dividend | Being divided | “What is being split?” |
| Divisor | Dividing number | “Into how many parts?” |
| Quotient | Result | “How much per part?” |
🧠 Quick Trick:
Dividend comes first in division just like it comes first alphabetically among the three.
Alternate Meanings of the Word “Dividend”
Outside of math, dividend has another very common meaning.
In Finance & Business
A dividend is:
A payment made by a company to its shareholders from profits.
Example:
“The company paid a quarterly dividend to investors.”
📌 Important:
While the word is the same, financial dividends and math dividends are different concepts, though both involve distribution.
Professional or Simpler Alternatives
In informal teaching settings, you might hear:
- “The number being divided”
- “The total”
- “The starting number”
These aren’t technical replacements but they help beginners understand the idea before introducing formal terminology.
Real-World Applications of the Dividend Concept
Understanding dividends helps in everyday situations:
- Splitting bills at restaurants 🍽️
- Sharing items equally among people
- Calculating averages
- Understanding fractions and percentages
- Programming and algorithms
Division is everywhere and the dividend is always at the center of it.
Final Thoughts and Practical Tips
If division ever feels confusing, go back to basics:
- Identify the dividend
- Identify the divisor
- Then calculate the quotient
Mastering the meaning of dividend builds a strong math foundation that supports everything from simple homework to advanced problem-solving.
📘 Tip for students:
When stuck, rewrite the problem and label each part it works every time.
Conclusion
Understanding what does dividend mean in math is a small concept with a big impact. The dividend is simply the number being divided, yet recognizing it correctly makes division problems clearer, more logical, and easier to solve. From basic arithmetic to fractions, algebra, and real-world problem solving, the dividend plays a central role in how numbers are shared and calculated.
By learning how to identify the dividend, divisor, and quotient, you build a strong foundation that supports more advanced math skills. Whether you are a student learning division for the first time, a parent helping with homework, or an adult refreshing math basics, mastering this term improves both confidence and accuracy.
FAQs
What does dividend mean in math for kids?
A dividend is the number you divide in a math problem. If you divide 10 by 2, then 10 is the dividend.
Is the dividend always the bigger number?
Usually, yes but not always. In fractions or decimals, the dividend can be smaller than the divisor.
Where is the dividend written in long division?
The dividend is written inside the long division symbol.
What is the dividend in a fraction?
The dividend is the numerator (top number).
Can a dividend be negative?
Yes. Dividing negative numbers still involves a dividend.
What happens if the dividend is zero?
If the dividend is zero, the quotient is always zero (as long as the divisor isn’t zero).
Is dividend used in algebra?
Absolutely. In algebra, the dividend can be a variable, expression, or polynomial.
What’s the difference between dividend in math and finance?
In math, a dividend is a number being divided. In finance, it’s a profit payment to shareholders.

Michael Jordan is a writer at ValneTix.com who explains word meanings in a clear and easy to understand style, helping readers expand their vocabulary and language skills.