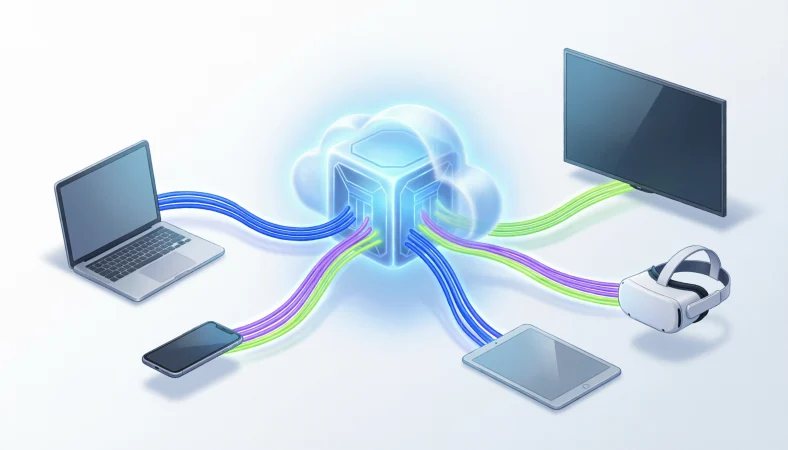
Headless software refers to applications, content management systems (CMS), or platforms that operate without a built-in front end interface. Instead of handling both the back end logic and the user facing interface, headless software focuses solely on managing data, logic, and content delivery, allowing developers to connect it to any front end presentation layer via APIs.
In simpler terms: a headless system “has no head” (user interface) and lets you decide how and where to show the content or application.
In today’s multi device world, software isn’t just consumed on desktops. People use smartphones, smartwatches, smart TVs, voice assistants, and even AR/VR devices. Traditional software platforms, where the back end and front end are tightly coupled, often struggle to deliver content seamlessly across these diverse channels.
This is where headless software comes in. By decoupling the back-end from the front end, it gives developers ultimate flexibility, faster delivery, and a more scalable digital experience.
Whether you’re a developer, business owner, or tech enthusiast, understanding headless software is essential to stay ahead in the modern tech landscape.
The Origin of “Headless” in Software 🏛️
The term “headless” originated in the web development and content management world in the 2010s. It was inspired by the concept of decoupling: separating the “head” (front-end) from the “body” (back-end).
- Traditional CMS like WordPress or Joomla provided a front-end and back-end together.
- Headless CMS like Contentful or Strapi focused only on content management, leaving the front-end to be built in frameworks like React, Angular, or Vue.js.
Over time, the concept expanded beyond CMS to e-commerce platforms, IoT devices, and automation systems, emphasizing flexibility and omnichannel delivery.
How Headless Software Works: Simplified Explanation
Think of a headless system as a “content or logic engine” that outputs information through APIs (Application Programming Interfaces). The front-end—your website, app, or digital display—fetches that data and presents it however it wants.
Key Components:
| Component | Role | Example |
| Back-End (Headless) | Manages content, logic, and data | Strapi, Contentful, Shopify (headless mode) |
| API | Delivers data to front-end | REST, GraphQL |
| Front-End (Headed by Developer) | Displays content/UI | React, Angular, Flutter, iOS/Android apps |
This separation allows the back-end to focus on storage and logic, while the front-end can innovate freely without being restricted by platform templates.
Popular Types of Headless Software
- Headless CMS
- Focus: Content creation, storage, and delivery.
- Examples: Contentful, Strapi, Sanity.
- Use case: Delivering blog content to a website, mobile app, or smart display simultaneously.
- Focus: Content creation, storage, and delivery.
- Headless E-Commerce Platforms
- Focus: Product catalog, inventory, and purchase logic.
- Examples: Shopify Plus (headless mode), Commerce Layer, BigCommerce.
- Use case: Selling products seamlessly across web, mobile, and social media.
- Focus: Product catalog, inventory, and purchase logic.
- Headless Automation & IoT Platforms
- Focus: Control devices or systems without a built-in UI.
- Examples: Home automation hubs, API-driven robotics platforms.
- Use case: IoT sensors sending data to dashboards, apps, or dashboards.
- Focus: Control devices or systems without a built-in UI.
Why Headless Software is Gaining Popularity 🚀
- Omnichannel Delivery: One system can power a website, app, IoT device, or digital signage.
- Flexibility for Developers: Freedom to choose any technology stack for the front-end.
- Scalability: The back-end can scale independently of the presentation layer.
- Improved Performance: No monolithic front-end slows down the system.
- Future-Proofing: Adapt easily to new platforms and devices without changing the back-end.
Example:
A brand using headless CMS can push product content to their website, mobile app, in-store kiosks, and AR experience without creating multiple back-end systems.
Headless vs Traditional (Coupled) Systems
| Feature | Traditional/Coupled | Headless |
| Front-End | Tightly integrated | Decoupled |
| Flexibility | Limited to templates | Fully customizable |
| Device Delivery | Mostly web | Web, app, IoT, AR/VR |
| Development Speed | Slower for multi-channel | Faster for omnichannel |
| Example | WordPress, Magento (classic) | Contentful, Shopify Headless |
💡 Tip: If your business only needs a single website with minimal updates, a traditional system might still suffice. Headless shines when delivering to multiple platforms.
Real-World Examples of Headless Software 🌎
- Contentful: Powers websites, mobile apps, and digital kiosks for brands like Spotify and Nike.
- Shopify (Headless): Lets e-commerce businesses build unique front-ends using React or Vue.js.
- Strapi: Open-source headless CMS that integrates with websites, apps, and APIs for seamless data flow.
Negative Perspective:
Some developers find headless systems more complex to implement than traditional CMS. There’s no built-in front-end, meaning you must build the presentation layer from scratch, which can be time-consuming for small teams.
Alternate Meanings of Headless
While in software “headless” mostly refers to decoupling, it can also mean:
- Headless Browser: A web browser without a GUI, used for automated testing and scraping (e.g., Puppeteer, Selenium).
- Headless Mode in Games/Applications: Running software without a graphical interface, often for performance or automation purposes.
Pro Tip: Always clarify the context: “headless CMS” vs “headless browser” vs “headless mode.”
Best Practices for Using Headless Software ✅
- Plan your API structure carefully.
- Decide on your front-end framework before implementation.
- Ensure security for API endpoints.
- Monitor performance across all channels.
- Keep content modeling flexible to support future platforms.
FAQs
- What is a headless CMS?
A headless CMS is a content management system that delivers content via API, without a built-in front-end. - Is headless better than traditional CMS?
It depends on your needs. Headless offers flexibility and multi-platform delivery, while traditional CMS is easier for simple websites. - Can headless software work with any front-end?
Yes! You can connect it to websites, apps, IoT devices, or even VR interfaces using APIs. - What programming languages are compatible with headless CMS?
Any language that can consume APIs, including JavaScript, Python, Ruby, PHP, and Java. - Are headless systems more expensive?
Implementation can be costlier initially due to custom front-end development but can save money in the long term via scalability. - What is the difference between headless and decoupled CMS?
Both separate back-end and front-end, but decoupled CMS may include some front-end features, while headless is fully front-end agnostic. - Is Shopify a headless CMS?
Shopify is primarily an e-commerce platform, but in headless mode, it functions similarly by providing APIs to power custom front-ends. - Can I switch from traditional CMS to headless?
Yes! Many platforms offer migration tools, but it requires careful planning for API structure and front-end development.
Conclusion
- Headless software removes the “head” (UI), focusing on back-end logic, content, or data management.
- It enables multi-platform delivery, developer flexibility, and scalability.
- Popular types include headless CMS, headless e-commerce platforms, and headless automation systems.
- While more complex to implement, headless software is future-proof and ideal for omnichannel experiences.
- Always consider your business goals before choosing headless vs traditional systems.
Pro Tip: Start small with a headless CMS or e-commerce system for one channel, then scale to multiple platforms gradually.

Alex Ferguson is a word enthusiast at ValneTix.com who turns the meanings of everyday words into fascinating discoveries. His articles make learning language easy, enjoyable and practical for all readers.