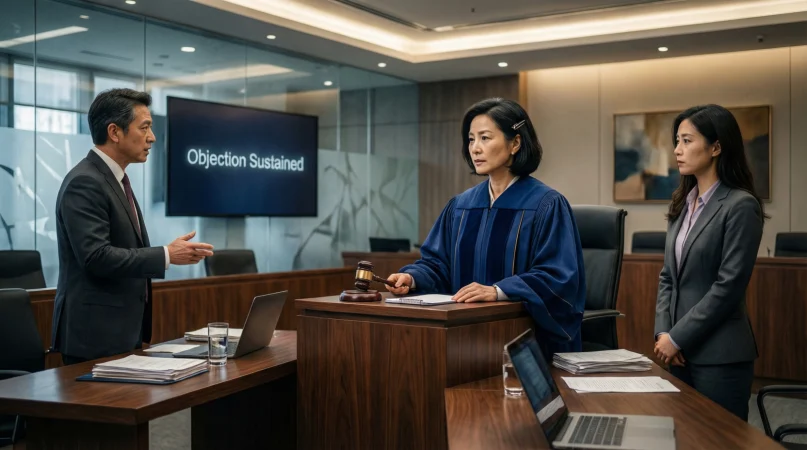
In court, “sustain” means that a judge agrees with an objection raised by a lawyer, deciding that the objection is valid and that the question, evidence, or statement challenged cannot be used or must be changed.
If you’ve ever watched a courtroom drama or followed a real legal case, you’ve probably heard the judge say, “Objection sustained.” It sounds dramatic but what does it actually mean? More importantly, what happens next when an objection is sustained in court?
This guide breaks it all down in plain English. Whether you’re a student, a curious viewer, or someone involved in a legal case, you’ll leave with a crystal clear understanding of what “sustain” means in court, how it’s used, and why it matters.
What Does “Sustain” Mean in Court?
In legal proceedings, to sustain an objection means:
- The judge agrees with the objection
- The challenged question, answer, or evidence is disallowed
- The lawyer must rephrase the question, move on, or stop that line of questioning
Simple way to remember it:
Sustain = Objection accepted
When a judge sustains an objection, it’s a signal that the courtroom rules were about to be broken—or already were.
Quick Courtroom Example
Lawyer: “Isn’t it true that the defendant was fired from his last job for dishonesty?”
Opposing Lawyer: “Objection, relevance.”
Judge: “Sustained.”
👉 Result: The question cannot be answered, and the jury (if present) is instructed to ignore it.
Why “Sustain” Matters in Court
“Sustain” plays a huge role in ensuring:
- Fair trials
- Admissible evidence only
- No misleading or prejudicial statements
- Procedural rules are followed
Without objections—and judges sustaining them—courtrooms would quickly become chaotic and unfair.
Origin and History of the Term “Sustain”
The word sustain comes from the Latin sustinere, meaning:
- to hold up
- to support
- to uphold
In law, this meaning evolved naturally. When a judge sustains an objection, they are literally upholding it.
Why the term stuck:
- Clear authority
- Formal tone
- Works across common law systems (US, UK, Canada, etc.)
How Popular Is the Term “Sustain” in Legal Usage?
“Sustain” is one of the most frequently used courtroom terms, especially in:
- Trials
- Hearings
- Depositions
- Moot courts
- Law school simulations
It’s also widely known due to:
- TV shows (Law & Order, Suits, Judge Judy)
- Real-life court coverage
- Social media legal commentary
How “Sustain” Is Used in Real Courtrooms
Typical courtroom flow:
- A lawyer asks a question
- Opposing lawyer objects
- Judge rules:
- “Sustained” or
- “Overruled”
That’s it. One word—big impact.
Common Types of Objections That Get Sustained
Judges sustain objections for many reasons, including:
- Relevance – Not related to the case
- Hearsay – Second-hand information
- Leading – Suggesting an answer
- Speculation – Witness guessing
- Asked and answered – Repeating the same question
- Argumentative – Lawyer arguing instead of asking
Labeled Example Table: “Sustain” in Action
| Situation | Objection Raised | Judge’s Ruling | Result |
|---|---|---|---|
| Lawyer asks irrelevant question | “Objection, relevance” | Sustained | Question struck |
| Witness speculates | “Objection, speculation” | Sustained | Answer ignored |
| Lawyer leads witness | “Objection, leading” | Sustained | Question rephrased |
| Improper evidence offered | “Objection, inadmissible” | Sustained | Evidence excluded |
Tone and Context of “Sustain” in Court
“Sustain” itself is neutral and formal, but the context can feel different depending on the situation.
Neutral / Procedural Tone
“Objection sustained. Please rephrase.”
Firm / Dismissive Tone
“Sustained. Move on, counsel.”
Protective Tone (Jury Trials)
“Sustained. The jury will disregard that statement.”
No emojis in real court—but plenty of emotional weight ⚖️
What Happens After an Objection Is Sustained?
Once an objection is sustained:
- The question cannot be answered
- Any answer already given may be stricken from the record
- The jury may be instructed to ignore it
- The lawyer must change strategy
Sometimes, a sustained objection can completely derail a line of questioning.
What Does NOT Happen When an Objection Is Sustained
Let’s clear up common myths:
❌ It does not mean someone is guilty
❌ It does not end the case
❌ It does not punish the lawyer
❌ It does not automatically favor one side long-term
It simply enforces courtroom rules—nothing more, nothing less.
Comparison: Sustain vs Overrule
| Term | Meaning in Court | Who Wins the Objection? |
|---|---|---|
| Sustain | Objection accepted | Objecting lawyer |
| Overrule | Objection rejected | Questioning lawyer |
Easy memory trick:
- Sustain = Stop
- Overrule = Proceed
Related Legal Terms and Abbreviations
- Objection – Formal challenge to a question or evidence
- Strike the record – Remove from official transcript
- Admissible – Allowed in court
- Inadmissible – Not allowed
- Bench ruling – Judge’s immediate decision
Alternate Meanings of “Sustain”
Outside court, sustain has different meanings:
- To maintain (sustain energy)
- To support (sustain a cause)
- To endure (sustain damage)
⚠️ But in court, it almost always means agreeing with an objection.
Professional or Polite Alternatives to “Sustain”
Judges rarely use alternatives, but in written rulings you might see:
- “The objection is granted”
- “The court upholds the objection”
- “The motion is approved” (not exactly the same, but related)
Still, “sustained” remains the gold standard in spoken court proceedings.
Usage Tips for Students, Writers, and Viewers
- Don’t confuse sustain with supporting a person
- Always pair it with “objection” in legal contexts
- Use it sparingly in writing—too much legal jargon can confuse readers
- If quoting dialogue, keep it short and realistic
FAQs
What does “objection sustained” mean in simple words?
It means the judge agrees with the objection and disallows the question or evidence.
Is sustaining an objection good or bad?
It’s good for the lawyer who objected and neutral for the case overall.
Can a judge sustain their own objection?
Yes. Judges can stop improper questions even without an objection.
What happens if an objection is sustained after an answer is given?
The answer may be stricken, and the jury told to ignore it.
Does sustained mean the case is over?
No. It only affects that specific question or evidence.
Why do judges say “sustained” instead of explaining?
For efficiency. Courts move fast and rely on standard terms.
Can a lawyer argue after an objection is sustained?
Sometimes, but usually only briefly or outside the jury’s presence.
Is “sustain” used outside criminal trials?
Yes. It’s common in civil trials, hearings, and administrative courts.
Conclusion
- “Sustain” means the judge agrees with an objection
- It blocks a question, answer, or evidence
- It helps maintain fairness and legal procedure
- It’s neutral, formal, and extremely common
- Best remembered as: Sustain = Objection accepted
If you’re watching a trial, studying law, or just love understanding legal language, knowing what “sustain” means in court gives you instant clarity and makes courtroom moments far less confusing.

Madison Lee is a skilled writer at ValneTix.com dedicated to making word meanings clear, relatable and actionable. She empowers readers to understand language deeply and use words with confidence in daily life.